Motorcycle Plastic Injection Molding is a pivotal process in the motorcycle industry. According to a recent report from Market Research Future, the global market for plastic injection molding in motorcycles is projected to reach $2 billion by 2025. This growth stems from the increasing demand for lightweight parts that enhance fuel efficiency and performance.
Dr. Emily Chen, an expert in polymer engineering, notes, "Innovation in Motorcycle Plastic Injection Molding is reshaping how we design and manufacture parts." Her insight highlights the importance of this technology.
However, challenges persist in the industry. Many manufacturers struggle with process optimization and quality control. Consequently, maintaining sustainability remains a concern. The journey of mastering Motorcycle Plastic Injection Molding is complex. Improvements are essential for the industry's future, making adaptation crucial.

Motorcycle plastic injection molding is a key manufacturing process for producing various motorcycle parts, including fairings, fenders, and grips. This method offers high precision and efficiency, utilizing thermoplastics that can be melted and shaped into complex forms. In the motorcycle industry, the demand for lightweight yet durable components keeps increasing. According to recent studies, the global plastic injection molding market for automotive applications, including motorcycles, is projected to reach $40 billion by 2026.
During the process, plastic pellets are heated until they become molten. This liquid plastic is then injected into molds under high pressure. After cooling, the solidified part is removed. While this method is effective, there can be issues like inconsistent wall thickness or air pockets trapped in the molds. Advanced monitoring systems help detect defects early, but the challenge persists. Approximately 10-15% of molded parts can fail quality checks, highlighting the need for continual improvements in techniques and materials.
Sustainable practices are also under scrutiny in this sector. As a result, manufacturers are exploring biodegradable plastics and recycled materials. However, the quality of these alternatives often raises questions. Ensuring the parts maintain functionality while adhering to sustainability goals remains a significant challenge for many in the industry.
| Aspect | Description | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process Overview | Plastic pellets are heated until melted and then injected into a mold to form parts. | High efficiency and reproducibility in producing complex shapes. | Covers parts such as fairings, body panels, and dashboard components. |
| Materials Used | Common materials include ABS, polypropylene, and nylon. | Durable and lightweight, suitable for dynamic uses. | Used in aesthetic and functional motorcycle components. |
| Mold Design | Molds must be precisely designed for optimal injection and cooling. | Allows for intricate details and tighter tolerances. | Critical for performance in parts such as engine covers. |
| Cost Efficiency | Initial tooling costs are high, but mass production lowers overall cost. | Economical for large-scale production runs. | Ideal for popular motorcycle models with high demand. |
| Environmental Impact | Utilizes recyclable materials which reduces waste. | Promotes sustainability within the industry. | Encouraged for eco-friendly motorcycle production practices. |
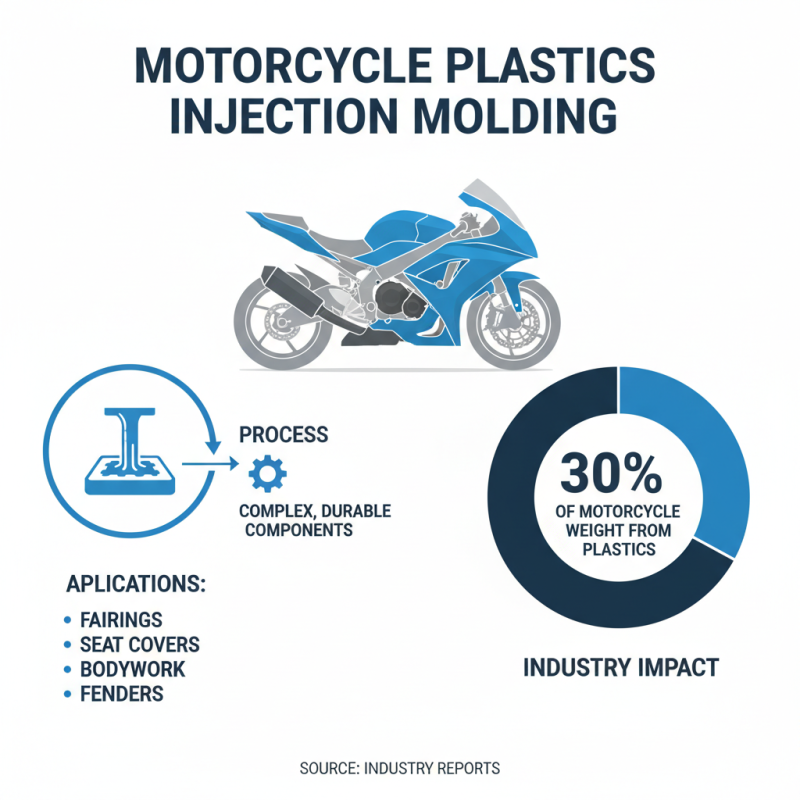
Motorcycle plastic injection molding is a crucial process in the manufacturing industry. This method allows for the creation of complex, durable plastic components. In motorcycle production, these parts often include fairings, seat covers, and other bodywork. According to industry reports, around 30% of a motorcycle's weight can come from plastic components formed by this technique.
The process begins with heating plastic granules until they melt. The molten plastic is then injected into a mold, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. This method offers precision and flexibility, enabling manufacturers to produce intricate designs that would be hard to achieve using traditional methods. However, some challenges exist, such as the need for high initial investment in molds. Additionally, the waste generated during the process can be significant, affecting overall efficiency.
Despite its advantages, motorcycle plastic injection molding faces criticism. The lifecycle of plastic components raises environmental concerns. Reports state that about 23% of plastic waste comes from the automotive industry. As manufacturers adopt more sustainable practices, the focus will shift to recycling and reducing waste. The industry must reflect on how to innovate while addressing these challenges.
Motorcycle plastic injection molding is a process that shapes various components for motorcycles. It involves melting plastic and injecting it into molds. The materials used are crucial for the success and performance of these parts. Most commonly, manufacturers rely on thermoplastics like polypropylene (PP) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Reports indicate that approximately 50% of motorcycle components are made from these materials due to their durability and flexibility.
For specific applications, materials like polyamide (PA) and polycarbonate (PC) are also popular. PA offers strength and resistance to wear, while PC provides excellent impact resistance. The industry statistics show that the demand for these materials is growing by around 8% annually. However, choosing the right material can be challenging. There is often a trade-off between cost and performance, leaving manufacturers to rethink their choices constantly.
In addition to performance, environmental impact plays a role in material selection. More companies are exploring biodegradable plastics. However, these alternatives may not always meet performance standards. Industry reports highlight that many manufacturers are still hesitant about switching, despite a growing consumer demand for sustainable options.
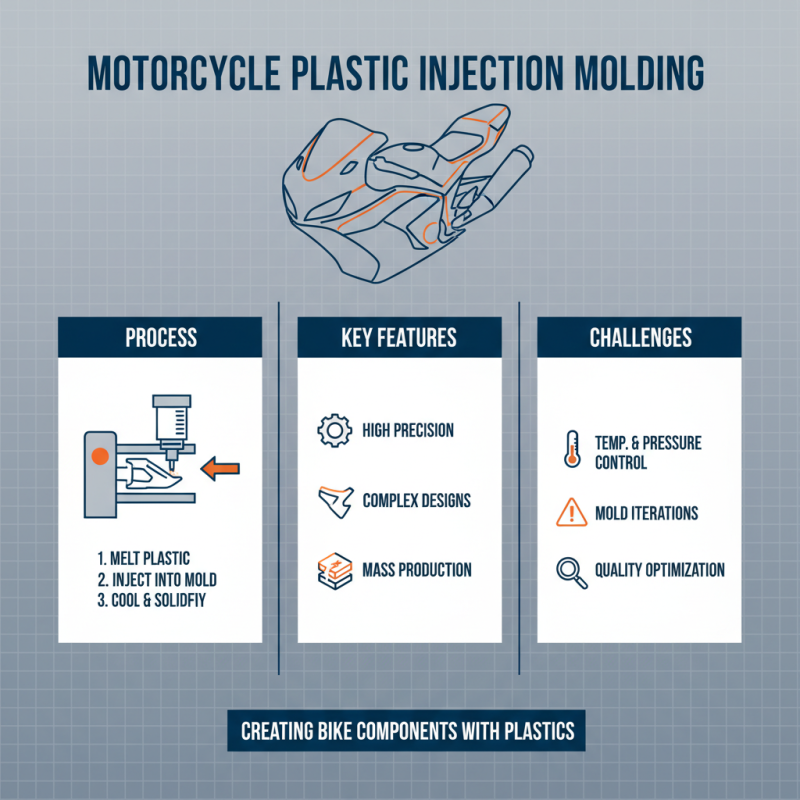
Motorcycle plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process used to create various components of motorcycles. This technique allows for high precision and detailed designs. The process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold, which then cools and solidifies. However, achieving the perfect mold can be tricky and sometimes requires multiple iterations. Manufacturers need to consider various factors like temperature and pressure to achieve desired results.
One of the significant advantages of this method is efficiency. It allows for mass production of motorcycle parts in a short time. This means more components can be made to meet increasing demands. Additionally, plastic injection molded parts tend to be lightweight and durable, which enhances the overall performance of motorcycles. However, it's crucial to recognize that not all designs work seamlessly with this method. Some intricate features may require careful planning and testing.
Cost-effectiveness is another major benefit. This method often leads to lower production costs compared to traditional manufacturing. Yet, the initial setup costs for molds can be high. Companies must balance these costs against potential savings in mass production. There is a fine line between quality and cost that needs constant evaluation.
Motorcycle plastic injection molding is crucial in manufacturing lightweight and durable components. Several parts benefit from this process, including fairings, fenders, and electrical housings. The industry report by Allied Market Research indicates that the global motorcycle plastics market is projected to reach $6 billion by 2026, driven largely by the rise in motorcycle usage in developing countries.
Fairings, molded from robust plastic, enhance aerodynamics and aesthetic appeal. They contribute to better fuel efficiency and improved rider experience. Moreover, electrical housings must be resistant to temperature fluctuations, moisture, and vibration. Injection molding offers precision and consistency, vital for complex designs. However, many manufacturers face challenges with material waste and recycling. Current molding techniques often leave behind excess plastic, which can be an environmental concern.
Fenders serve both functional and aesthetic purposes. Molded plastic fenders are lighter than metal ones, improving handling and performance. Nonetheless, the lifecycle of these parts requires scrutiny. While they reduce weight, the durability of molded plastics can be inconsistent. Some users report cracking or fading after prolonged exposure to UV rays. Addressing these issues should be a priority for manufacturers to ensure sustainable practices in the motorcycle industry.